Ignition System Requirements
Ignition System
The purpose of the ignition system is to generate a very high volt age from the car's 12 volt battery, and to send this to each sparkplug in turn, igniting the fuel-air mixture in the engine 's combustion chambers. The coil is the component that produces this high voltage. An Ignition Interlock Limited License permits an individual, if certain requirements are met, to operate a motor vehicle(s) equipped with an Ignition Interlock system during the term, or part of the term, of their suspension or revocation.
For burning any fuel we need two things. First is oxygen and second is heat.
Fuels which has self ignition temperature can even be burnt with applying high pressure, like Diesel. But the case of petrol or gasoline is different.
In a spark ignition engines, compression ratio is lower, and self ignition temperature of petrol is higher. Hence to ignite the mixture for the initiation of combustion an ignition system is must.
Requirements of an ignition system
- It should provide good spark at correct timing.
- It should function efficiently for all engine speeds.
- It should be light, effective and reliable in service.
- It should be compact and easy to maintain.
- It should be cheap and convenient to handle.
- The magnetic field generated from the voltage source of the ignition system should not affect radio and television inside the automobile.
There are basically two types of ignition systems are used in automobiles. One is battery ignition system and another one is magneto ignition system.
Lets first discuss battery ignition system
Battery Ignition System
In a battery ignition system, a battery is used as a source of energy for the spark plug. This battery is rechargeable and derives energy for its recharging from an alternator.
This alternator is connected from the crankshaft of the engine and converts its mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Essential components of battery ignition system


- Battery
- Ignition switch
- Ballast resistor
- Ignition Coil
- Contact breaker
- Capacitor
- Distributor
- Spark plug
Characteristics battery ignition system
- Battery is necessary. Difficult to start the engine when battery is discharged.
- Maintenance problem is more due to battery.
- Power for ignition is obtained from the battery.
- Good spark is available, even at low engine speed.
- As engine speed increases, efficiency of battery ignition system decreases.
- Occupies more space.
- Commonly employed in cars and light commercial vehicles.
Magneto ignition system
A magneto ignition system uses its own electric generator instead of a battery to derive power for electric spark.
Ignition Edge System Requirements
All the parts of battery ignition system replaced except spark plug.
Characteristics magneto ignition system
- No battery is needed and therefore no problem of battery discharge.
- Maintenance problem is less, as there is no battery.
- The power for producing spark is obtained from magneto.
- At low speed efficiency of magneto ignition system is low.
- As speed increases the efficiency of magneto ignition system increases.
- Occupies less space
- Mainly used in racing cars and two wheeler.
Image (also featured) attribution: By Andy Dingley (scanner) – Scan from (1911) Mechanical Transport, HMSO, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=9884580
The Video Course teaches you everything about modern cars.
Inspect the ignition system whenever you make a general under-bonnet check. It takes only a couple of minutes, and guards against a frequent cause of breakdown.
Check that the low-tension connections are tight and free from corrosion, and that all LT wires have sound insulation and no cracks, kinks or breaks.
Follow with the plug leads and plugs. The leads should be clean, dry and free from cracks or kinks.
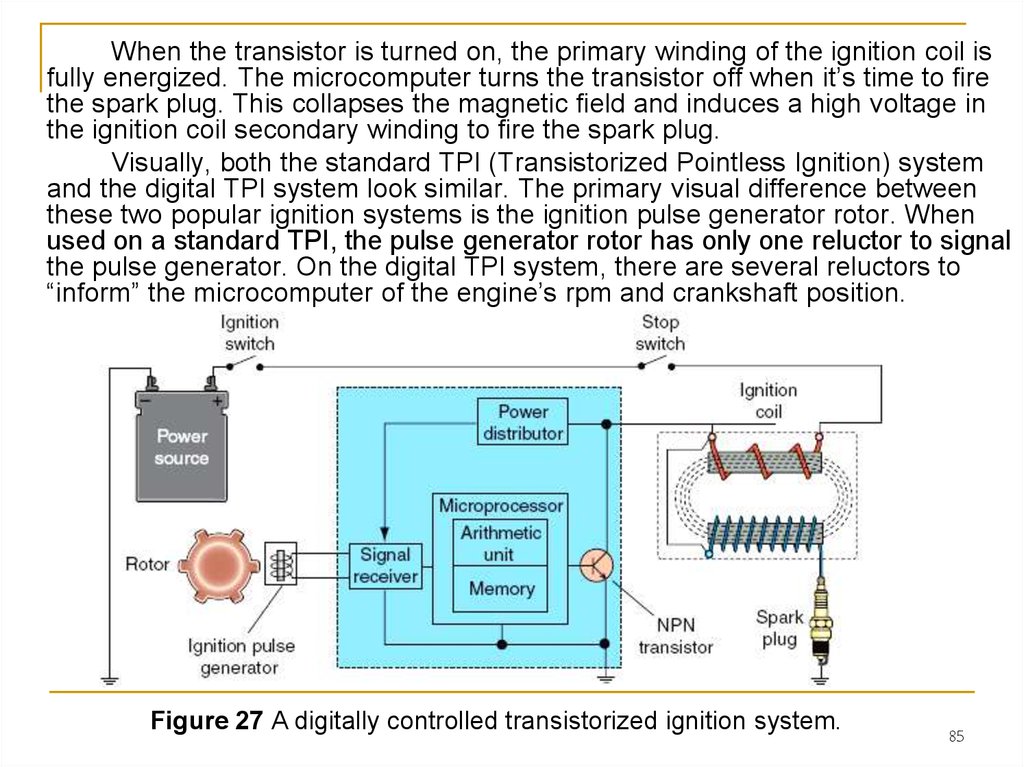
Ignition System Diagram
If there are special guide clips, the leads should run inside them: the clips are to keep them away from each other and from hot surfaces.
Clean the leads with a soft cloth. Replace them if they are damaged or if the wrong type has been fitted at some time. High-tension leads should be replaced every two or three years, to maintain peak performance (See Fitting new high-tension leads).
Check that the plug caps are firmly fixed to the leads, and that the leads are properly connected to the distributor.
Take care not to get the connections mixed up — tag them with sticky tape if necessary.
Leads may be screwed into the distributor vertically with threaded collars; pushed in vertically and held by crimped terminals; or inserted from the side and held by small screws.
Check the distributor and plug caps for cracks. Pull off the plug caps one at a time — pulling the cap, not the easily damaged lead — and wipe the porcelain plug tops.
Ignition 8.1 System Requirements
Take off the distributor cap. It may have a pair of spring clips which you lever off outwards, or two small screws — avoid dropping these.

Check the inside of the cap for cracks. Look closely at the contacts.
If there is a sprung carbon brush at the top, it should be free to slide up and down; or there may be a spring contact on top of the rotor arm, which bears against a fixed carbon brush in the cap. The rotor-arm spring contact should be free from wear or damage.
The rotor-arm tip and the contacts around the inside of the cap should not be more than slightly pitted, and the gap between tip and contacts must not vary.
If the rotor-arm tip is dirty, lift off the arm (a few types have screws) and clean it by removing the pitting marks by gentle filing or scraping.
Remove any corrosion from the contacts inside the cap by gentle scraping.
The narrow pipe or pipes of the vacuum advance mechanism run from the distributor to the inlet manifold. Older cars have a metal pipe with a screwed union or a push-on rubber sleeve connector.
Most have a plastic pipe which is a push-on fit.
Check that the pipe is undamaged and that the connections are sound. A plastic pipe must be routed away from heat.
If you have any doubt about the soundness of the pipe or connections, only a stroboscopic timing test (See Stroboscopic timing) can make sure.
Look at the coil. The most usual type has a thick HT lead coming out of the end flanked by two smaller LT leads.

The HT lead may be a push-in fit or have a screw collar. Check that it is firmly fixed to both coil and distributor, and that any rubber seals over the ends fit properly.
Ignition Scada System Requirements
The LT leads have spade connectors, or screws on older cars. Make sure these are firmly fastened, and that the leads are connected the right way round: a coil connected backwards still works, but could cause a misfire.
5 Type Of Ignition Systems
On a modern negative-earth car the positive terminal, marked +, is connected to the ignition switch; the negative, marked —, to the contact-breaker points in the distributor.
For positive-earth cars — usually earlier models — they are connected the opposite way round.
Some terminals are marked 'SW' (switch) and 'CB' (contact breaker) usually on earlier cars.
Make sure that the coil is fixed firmly in its mountings.
Most coils have a ballast resistor — a small porcelain block containing a wire coil and connected by spade or screw terminals into the LT lead to the switch.
There are two leads from the switch to the coil; one for normal running going through the resistor; the other for starting, which bypasses the resistor to provide extra ignition strength.
The resistor is often clamped to one of the coil mounting bolts. Make sure it is not cracked, and that the connectors are tight. Some cars have a resistive lead from ignition switch to coil instead of a separate resistor.
The last part of the test is optional because you can only do it in the dark — but well worth the trouble. Start the engine and look for 'tracking' — leakage of high-tension electricity from the coil, distributor, HT leads or plugs, caused by damaged or wet insulation. It shows up as blue sparks.